The Plasma Physics Department in structure of the Scientific-Technical Center of Plasma Technologies unites group of scientific personnels of MRTI which within last two-three decades were engaged in studying of properties of gas-discharge processes and physical and chemical transformations in the condensed environments, occurring in fields of powerful concentrated electromagnetic radiation of MW range. Great volume of the saved up knowledge in this area and experience of the experimental and theoretical researches spent in interests of military-applied problems, has opened wide road for works on development of a spectrum of physico-technological appendices. To such, to the most perspective, directions in which development the essential contribution brings MRTI, it is possible to carry plasma aerodynamics, plasma burning, MW plasmatrons, updating of surfaces and synthesis of materials, reception of pulse plasma with extreme parameters (up to thermonuclear), etc
The New type of the discharge arising in focus at a distance from radiating systems outside of contact to any elements of designs (Fig.1), possesses remarkable properties which determine a variety of opportunities of its application.

The MW discharge of a high pressure develops in the form of a net of branching thin streamer channels. The electric field on the ends of channels repeatedly is exceeded with a field of a primary MW radiation, as determines ability of MW streamer discharges, having arisen in one place to extend beyond all bounds in gas with high pressure. Researches are conducted at various pressure of gas inside of the vacuum chamber. Such discharge can be observed directly in room air at the open casing of the vacuum chamber. During an impulse of 40 microseconds the discharge has time to run >10 cm, that, distribution there are to speed some kilometers a second. In the certain conditions the net of channels extends exclusively on a surface of a dielectric plate, a film or a fine grid if those to place in area of the discharge (Fig.2).
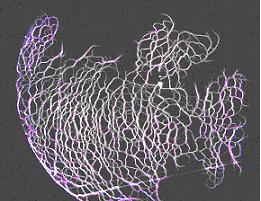
Similar researches are conducted also on installations with other lengths of waves. On installation with length of a wave 2.5 cm the discharge in focus of radiation is studied in a pulse-periodic mode. It also can be observed in room air at the open casing of the vacuum chamber. The discharge and at this length of a wave keeps the streamer nature, and its behavior is described within the limits of the same physical model, as discharge at greater wavelength.
The department of Plasma Physics is engaged in studying of properties of the MW discharges of a high pressure not only because this most interesting physical phenomenon. Its properties discovered during researches open new opportunities in a number of actual appendices. To such determining properties concern the following:
Heat in streamer channels in a combination to high efficiency of absorption of MW energy, their high speed of distribution have determined a direction of applied researches on initiation and stimulations of burning in various situations: in internal channels of combustion engines, in turbogaseous installations, turbojets, in direct-flow engines, hypersonic engines with supersonic burning. Use of the MW streamer discharge allows to support, basically, a stationary weak detonation wave in a stream of a gas mixture at speed, above speed of a free detonation wave (~1.5 km/s are usual). The direct-flow engine based on such mode, would possess a specific impulse, in some times greater, than in designed hypersonic devices
Studying of properties of MW discharges in a high-speed stream of air occurs at the aerodynamic stand in which working chamber the flooded jet of air (or combustible gas mixture) is created, In the flooded jet it is generated by means of the initiator the streamer discharge due to an external MW radiation. Speed of a jet can exceed speed of a sound twice (M=2). Here special types of initiators with reference to typical conditions of application in various devices are fulfilled and ways of submission of fuel, for example, through the internal channel of the initiator, as in shown experience, efficiency of burning at presence of the discharge both at a free stream of a gas mixture, and at the closed channel of the chamber of combustion are investigatedA>
Ability of MW discharge with high efficiency to carry out energy addition in a stream of gas in the set place concerning a body, flowed round by it, it is used for control of characteristics of a flow. On this installation fivefold reduction in frontal resistance of a cylindrical body in a stream with M=2 is shown at creation thin and hot streamer channel before a body with power efficiency, greater unit in times. Here occurrence of additional elevating force has been shown at allocation of energy by means of MW discharge under a streamline structure. Experiments have completely confirmed the theoretical calculations predicted found out effects which can be used for increase of a maneuverability and stability of flying devices at supersonic flight.
In the department the works on development of MW plasmatrons of various types are developed. All of them are based on the common principle of work. Working gas proceeds through the MW resonator in which the discharge which is heating up gas up to temperature of some thousand of degrees is lit. At so heat ionization of gas is high enough, that absorption of MW radiation, occured within the limits of a hot zone, so discharge is not demand a constant initiation. The organization of vortical movement in volume of the discharge chamber provides isolation of walls of the chamber and exit nozzle from hot gas that promotes essential increase in service life of plasmatron and significant simplification of its design. In plasmatrons such type hot jets in the wide range of parameters (temperature, speed, diameter, length and so forth) for use in the most different processes, including such actual, as recycling waste, burning difficultly burning fuels, in gasegenerators etc., can be achieved.
In a department the works on use of MW power radiation for synthesis of new types of ceramic and diverse materials are also conducted .
Successful promotion of research works is provided by a high professional level of department experts.
1. Burning poor gas mixtures for decrease of harmful emissions into atmosphere 2. Increase in speed of burning in channels of turbojet, direct-flow and hypersonic engine 3. Burning and gasification of low-calorie fuels 4. Recycling of waste Heating of gas in the certain places outside of the device which is flowed round by a high-speed stream, is capable to influence characteristics of a flow essentially. The MW are capable to carry out discharges such remote energy addition. It forms a basis for following work:
1. Development of methods of increase of controllability of flying devices in conditions of supersonic flight
2. Increase of an overall performance of turbines in turbojets and power installations
The direct-flow engine on a stationary detonation wave can have a specific impulse many times over above the values achieved nowadays.
EXPERIMENTAL BASE Contact information:
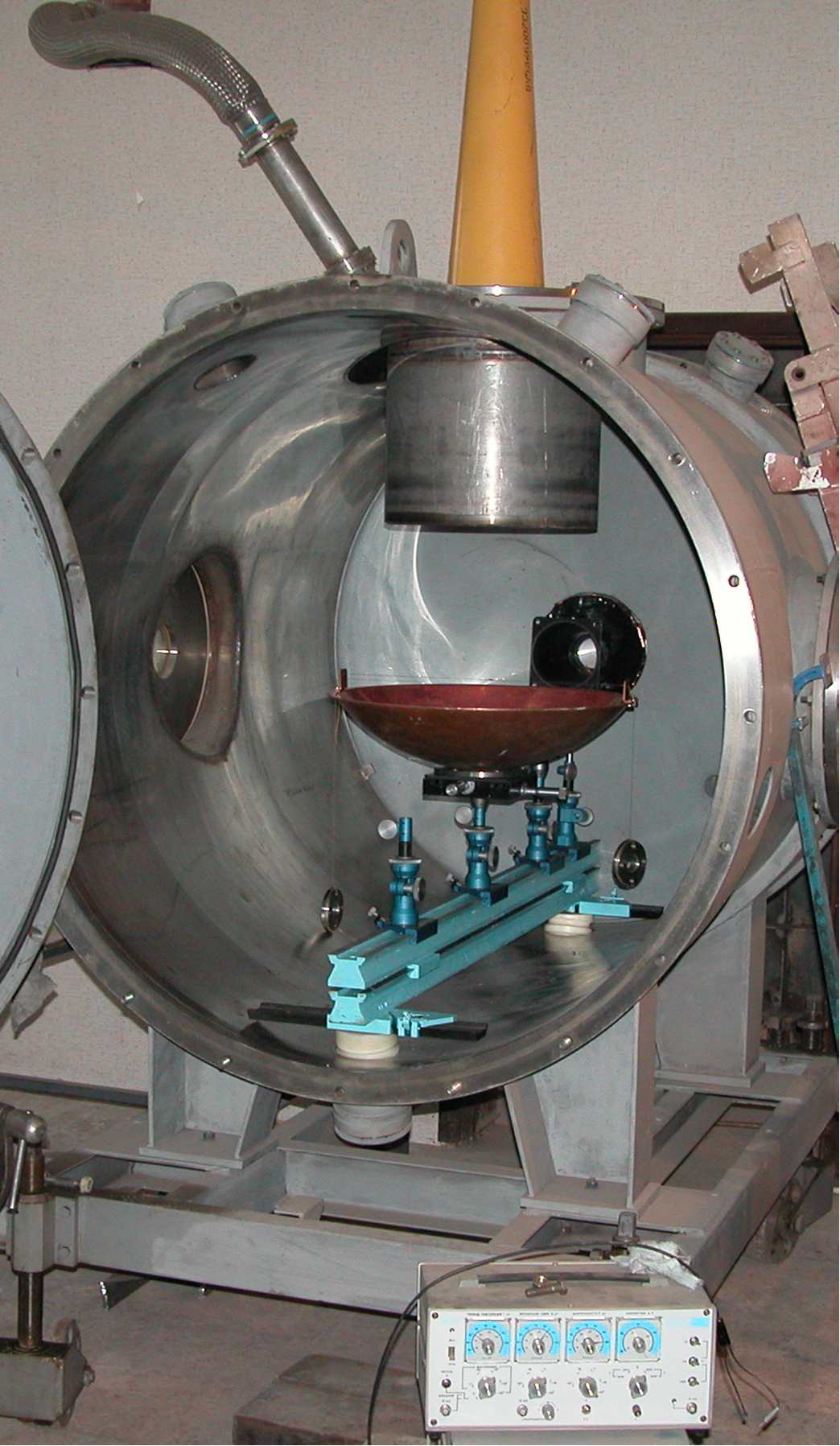


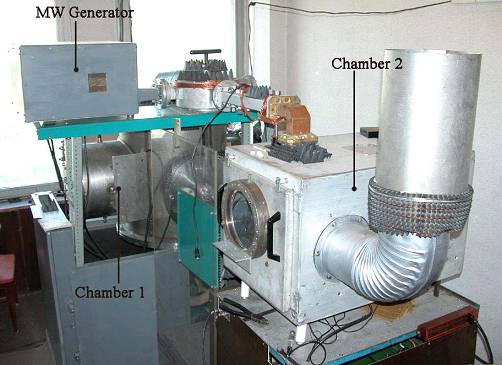
Email: K.V.K@home.ptt.ru
Web:http://www.kir-khodataev.narod.ruTel:
+7 (495) 315-2497 Fax: +7 (495) 314-1053
Mail address: Moscow Radiotechical Institute of RAS (MRTI), Warshavskoe shosse 132, Moscow, 113519, Russia